AI Data Privacy In 2026: 7 Secrets to Protecting Your Digital Identity
Imagine sitting in a private meeting or a quiet cafe, discussing a sensitive life event or a new business idea. You haven’t typed a single word into a search engine. Yet, an hour later, your social media feed is saturated with ads and “suggested content” that perfectly mirror your private conversation. This is not magic. It is the reality of AI data privacy in 2026.
Artificial intelligence has become an integral part of our everyday tools, shaping our searches, feeds, and recommendations with precision. For many readers, the practical question is no longer whether AI is watching. The question is straightforward: how does AI alter the fundamental principles governing personal information?
This guide focuses on AI data privacy in 2026. We will explain the critical risks and provide actionable steps that every digital user should take immediately. Understanding these systems is the first step toward reclaiming your digital autonomy. At Digital Solutions Edge, we believe that privacy is not just a right. It is a prerequisite for holistic success
Table of Contents
Why AI Changes the Privacy Game
AI systems need massive amounts of signals to learn. When we talk about AI data privacy in 2026, we mean the ways data is collected, combined, and reused to train models that operate long after an interaction ends.
In the past, data was stored in static databases. Today, your data is “ingested” into neural networks. This means your search queries, location history, voice commands, and biometric signals become part of the training fabric itself. Traditional anonymisation claims are no longer a guarantee because AI can re-identify individuals by connecting seemingly unrelated data points.
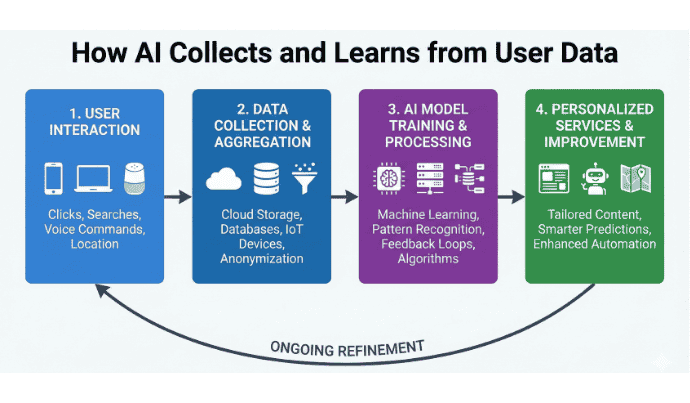
Diagram illustrating AI data collection
7 Secrets Every Digital User Must Know
1. Your Data Trains AI Systems, Often Without Clear Consent
Most consumer AI services rely on user data to improve models. In practice, AI data privacy in 2026 means assuming your public posts, uploads, and interactions can be used to train models unless you explicitly opt out. Companies are updating their policies and opt-in/opt-out flows (WIRED). For example, firms like Anthropic and OpenAI have introduced toggles that allow users to prevent their data from being used for training, but these are rarely the default setting.
Stay alert to policy updates. If a service is free, your data is likely the currency. To protect your AI data privacy in 2026, you must become a proactive auditor of every digital tool you use.
2. AI Systems Can Profile You With Unsettling Accuracy
Algorithmic profiling uses small behavioural clues to craft detailed profiles. In conversations about AI data privacy in 2026, profiling explains how firms personalise ads, offers, and even pricing.
AI does not just know what you did; it predicts what you will do next. By analysing the rhythm of your typing, the speed of your scroll, and your location patterns, AI can infer your health status, political leanings, and financial stability. This is why “anonymised” data is a myth.
Being aware of profiling is your first line of defence against unseen discrimination. When you understand that every click feeds a profile, you begin to treat your digital footprints with the respect they deserve.
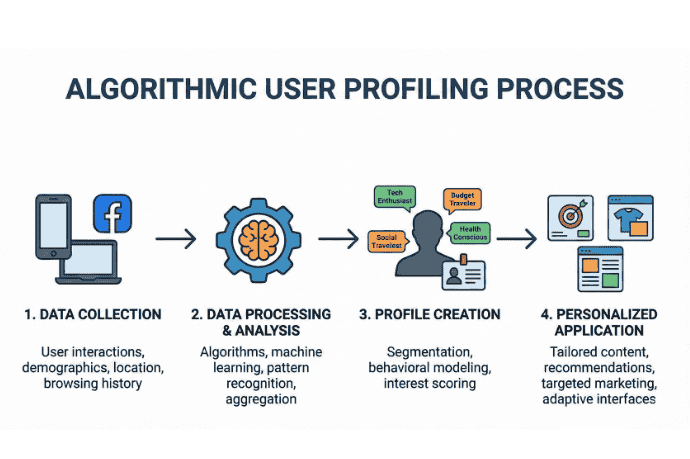
Visual showing algorithmic profiling
3. Data Breaches Now Involve Models Themselves
Data breaches in 2026 have evolved. Attackers no longer target raw databases. They now target the AI models themselves through “model inversion” and “extraction attacks.”
In a model inversion attack, a hacker can reverse-engineer an AI model to recover the specific data used to train it. This means if your medical records or private messages were used to train a model, a sophisticated attacker could potentially extract that information.
Recent academic research documented on arXiv shows that these attacks are becoming more viable as models grow in complexity. This shift makes AI data privacy in 2026 a high-stakes security issue for both individuals and organisations. (arXiv)
4. Regulation Is Evolving, But Not Evenly
Regulatory frameworks are shifting in 2026 to address AI data privacy concerns. However, these laws are not applied evenly across the globe. The EU’s AI Act provides a risk-based approach and new transparency requirements for high-risk systems; national laws (for example, recent moves in Italy) add further controls for privacy and minors. Enforcement timing varies, so user vigilance remains essential. (Digital Strategy)
5. Many Devices Are Listening, Literally
Smart speakers, wearables, and cameras generate continuous signals that factor into ML training. When evaluating device habits, remember AI data privacy involves both content and metadata. Even if a company does not “listen” to your words, they are recording your “usage rhythms.” Timestamps, location tags, and device handshakes reveal your daily patterns with terrifying clarity.

Smart speaker privacy settings
6. Surveillance Capitalism Is the Business Model Behind Personalisation
Behind “free” experiences is a trade: attention and behavioural signals for better targeting. Conversations about AI data privacy in 2026 highlight how companies monetise aggregated signals to predict and influence choices. Recognising this model helps you make deliberate trade-offs between convenience and control.
7. Users Have Real Tools to Reclaim Control
Despite the challenges, AI data privacy also offers paths back to user control. Demand transparency, choose privacy-first products, use opt-outs, and exercise your data rights. Collective actions like regulatory complaints or switching platforms shift corporate incentives.
Real-World Examples & Recent Developments
Companies and regulators are already adjusting practices in response to privacy pressures. For example, several major firms have announced changes to how they handle user content for training and added opt-out controls, reinforcing the urgency of AI data privacy for everyday users. (WIRED)
- Anthropic and other providers have updated settings that affect training data policies; check your account privacy toggles. (WIRED)
- Meta has engaged with EU data regulators and restarted limited uses of public content for training after regulatory review, underlining how AI data privacy remains contested. (AP News)
- National laws (for example, Italy’s new AI legislation) show how governments are responding to privacy and child-protection concerns tied to AI. (Reuters)
How to Safeguard Your Data in an AI-Driven World
Practical steps to protect yourself and reduce exposure to AI data privacy risks in 2026:
- Choose privacy-first tools. Use browsers, messaging apps, and email services that emphasise minimal retention and strong encryption. Use browsers like Brave, email services like ProtonMail, and search engines like DuckDuckGo.
- Audit app permissions monthly. Remove microphone, location, and contact access where it’s not essential; these permissions feed the signals that inform AI.
- Think before you upload. Avoid sending sensitive files to free AI tools; uploaded content may become part of training sets relevant to AI data privacy concerns.
- Use hardware 2FA for critical accounts. Even if your data is acquired, stronger account controls limit damage.
- Exercise data rights. Use opt-outs and deletion requests where available; keep records of correspondence for stronger legal claims related to AI data privacy.
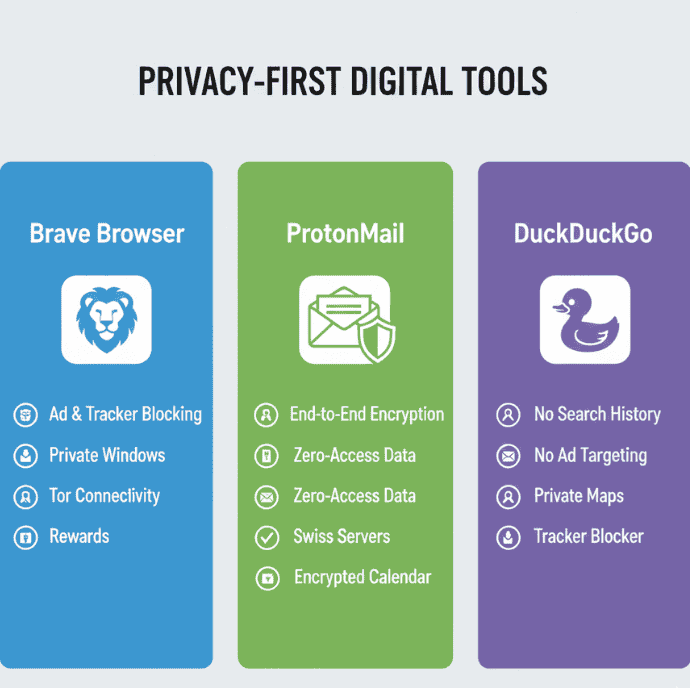
Comparison chart for privacy-first tools
Looking Ahead: The Future of Ethical AI & Data Ownership
Emerging technologies aim to reduce centralised exposure: federated learning, differential privacy, and data-control tokens. If adopted widely, they could improve AI data privacy outcomes by keeping raw data local and limiting what leaves a device. The pace of adoption will depend on regulation, industry economics, and public demand.
FAQs on AI and Data Privacy 2026
- Can AI tools access my private files or messages? Not by default, but integrations and permissions can grant access. Metadata can still be used for profiling; awareness is key when considering data privacy.
- Is AI regulation the same everywhere? No. The landscape of AI data privacy in 2026 is highly fragmented. The EU has the most stringent rules, while other regions are more permissive. You should research the specific laws in your country to understand your legal standing.
- How can I delete my data from AI systems? Most major AI providers now offer a “Data Deletion” or “Opt-Out” form. Under regulations like the GDPR, companies are legally obligated to process these requests. You can find these forms in the “Privacy” or “Settings” section of the respective platform.
- Are free AI tools safe? Free tools may retain and monetise content; treat free services cautiously in the context of AI data privacy.
- What’s the safest browser for AI privacy? Brave, Firefox, and Tor are solid choices for reducing tracking that exacerbates AI data privacy risks in 2026.
Quick Checklist: Immediate Actions for AI Data Privacy in 2026
- Review privacy settings now; focus on AI data privacy in 2026 when toggling model-sharing options.
- Opt-out or limit training data access to protect your content; prioritise AI data privacy in 2026 practices.
- Audit apps and permissions this week to reduce signals feeding models; a small step for AI data privacy in 2026.
- Keep records of deletion and opt-out requests to reinforce your rights in relation to AI data privacy in 2026.
Take Control of Your Digital Future
AI data privacy is a practical skill, not a philosophical debate. Start by auditing your apps, claiming available opt-outs, and choosing tools that respect user rights. When users insist on stronger privacy standards, industry habits change, and regulation follows. Your choices today shape the direction of data privacy for everyone.
Subscribe to Digital Solutions Edge for weekly insights on AI ethics, digital literacy, and future-proof productivity.
Share this article with someone who values their privacy, and keep exploring more resources to build digital awareness and data protection strategies with these helpful guides: Security SOPs and Templates to ensure your business follows best practices for data protection and compliance.
Tool Audit Checklist: a step-by-step guide to evaluate your current tech stack and remove redundant tools.
Automation Playbook explore ready-made automations and templates to boost team efficiency.
Protecting data privacy starts with small, practical habits.








Leave a Reply